背景
SSO,即 Small String Optimization。字面意思,面向小数据集场景(长度)进行的优化,以避免高额动态内存分配。
知名库——libstdc++/libc++/MSVC.STL/folly 均采用了不同的方式去实现 SSO。既然存在不同方式,那说明 SSO 没有任意场景的最优解。它们的 SSO 缓冲阈值是多少,为引入 SSO 而设计的字符串本身的静态内存布局占用多大,SSO 的引入是否会为基本使用(data()/size())带来额外的运行时开销,这些都是问题。
本文将快速总结 SSO 的实现方式,了解通用库是怎么选择的。
NOTES:
- 关于库版本,均为本文章发布日期的 master 版本。
- 为了版面简洁,会有部分精简实现,同时函数会直接内联。
- 不讨论 SSO 以外的事情。
libstdc++
结论先行
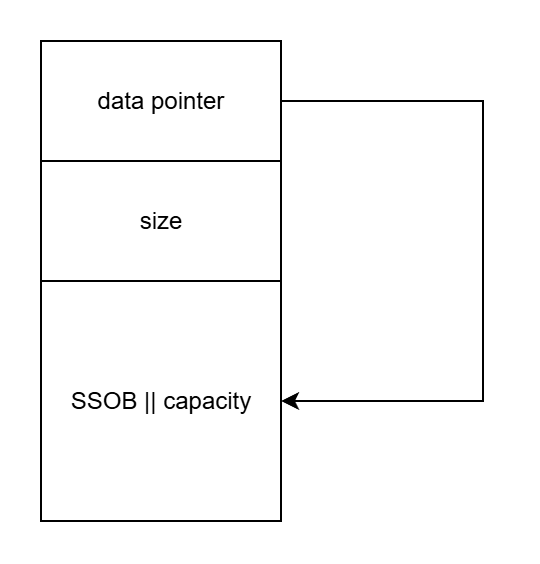
对于内存占用,libstdc++ 的 std::string 静态内存布局占用 32 字节(8+8+16),SSO 阈值为 16(含 '\0')。观察到 SSO 场景的 capacity 是固定的,它重用了 SSO buffer 和 capacity 来节省内存。
对于初始化的运行时内存布局,如果不超出 SSO 的范围,data pointer 将指向 SSO buffer;否则就需要高额的动态内存分配。
对于运行时开销,data() 和 size() 不受 SSO 影响,而 capacity() 总是需要一条额外的分支指令开销。反汇编在这里。(注:GCC 会生成 cmov 指令,而这里使用的 Clang 只有跳转。)
内存布局
template<typename _CharT, typename _Traits, typename _Alloc>
class basic_string
{
struct _Alloc_hider : allocator_type
{
pointer _M_p; // The actual data.
};
_Alloc_hider _M_dataplus;
size_type _M_string_length;
enum { _S_local_capacity = 15 / sizeof(_CharT) };
union
{
_CharT _M_local_buf[_S_local_capacity + 1];
size_type _M_allocated_capacity;
};
};
运行时布局
// 决定运行时布局的构造函数
// 假设是空状态
_GLIBCXX20_CONSTEXPR
basic_string()
: _M_dataplus(std::pointer_traits<pointer>::pointer_to(*_M_local_buf))
{
/// _M_init_local_buf():
// Ensure that _M_local_buf is the active member of the union.
if (std::is_constant_evaluated())
for (size_type __i = 0; __i <= _S_local_capacity; ++__i)
_M_local_buf[__i] = _CharT();
/// _M_set_length(0):
_M_string_length = 0;
_M_dataplus._M_p[0] = 0;
}
// 假设是来自一个字符串 const char*
_GLIBCXX20_CONSTEXPR
basic_string(const _CharT* __s, const _Alloc& __a = _Alloc())
: _M_dataplus(std::pointer_traits<pointer>::pointer_to(*_M_local_buf), __a)
{
const _CharT* __end = __s + traits_type::length(__s);
/// _M_construct(__s, __end, forward_iterator_tag()):
const _CharT* __beg = __s;
size_type __dnew = static_cast<size_type>(std::distance(__beg, __end));
if (__dnew > size_type(_S_local_capacity))
{
_M_data(_M_create(__dnew, size_type(0)));
_M_capacity(__dnew);
}
else
_M_init_local_buf();
this->_S_copy_chars(_M_data(), __beg, __end);
_M_string_length = __dnew;
_M_dataplus._M_p[__dnew] = 0;
}
NOTES:
- 为了版面我这里去掉了 noexcept(太长)。
- quux 指出这种指涉的做法并不符合 trivially relocatable 概念。
运行时开销
_GLIBCXX_NODISCARD _GLIBCXX20_CONSTEXPR
const _CharT*
data() const _GLIBCXX_NOEXCEPT
{ return _M_dataplus._M_p; }
size_type
size() const _GLIBCXX_NOEXCEPT
{ return _M_string_length; }
_GLIBCXX_NODISCARD _GLIBCXX20_CONSTEXPR
size_type
capacity() const _GLIBCXX_NOEXCEPT
{
return _M_data() == _M_local_data() ?
size_type(_S_local_capacity) : _M_allocated_capacity;
}
MSVC STL
结论先行
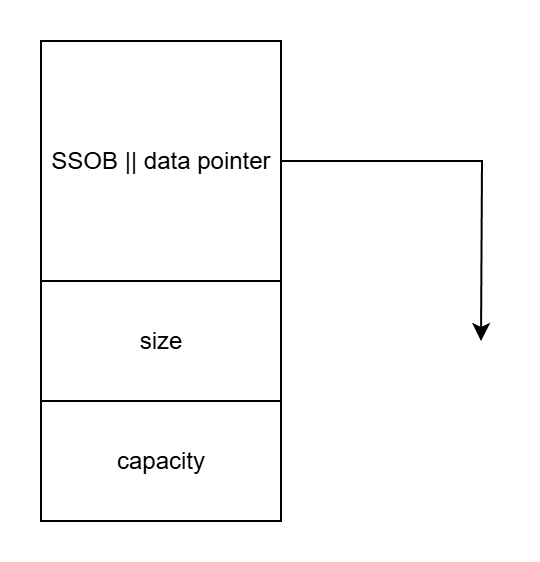
对于内存占用,MSVC STL 的 std::string 静态内存布局占用 32 字节(16+8+8),SSO 阈值为 16(含 '\0')。对比 libstdc++ 不同在于,MSVC STL 重用了 SSO buffer 和 data pointer 来节省内存。
对于初始化的运行时内存布局,如果不超出 SSO 的范围,data pointer 不需使用;否则就需要高额的动态内存分配。
对于运行时开销,data() 总是需要一条额外的分支指令开销,因为需要判断使用 SSO buffer 还是 data pointer。(高频接口加分支,微软这是想要干嘛啊)
内存布局
template <class _Elem, class _Traits = char_traits<_Elem>, class _Alloc = allocator<_Elem>>
class basic_string {
using _Alty = _Rebind_alloc_t<_Alloc, _Elem>;
using _Scary_val = _String_val<conditional_t<_Is_simple_alloc_v<_Alty>, _Simple_types<_Elem>,
_String_iter_types<_Elem, typename _Alty_traits::size_type, typename _Alty_traits::difference_type,
typename _Alty_traits::pointer, typename _Alty_traits::const_pointer>>>;
_Compressed_pair<_Alty, _Scary_val> _Mypair;
};
template <class _Val_types>
class _String_val : public _Container_base {
using value_type = typename _Val_types::value_type;
// length of internal buffer, [1, 16] (NB: used by the debugger visualizer)
static constexpr size_type _BUF_SIZE = 16 / sizeof(value_type) < 1 ? 1 : 16 / sizeof(value_type);
union _Bxty { // storage for small buffer or pointer to larger one
value_type _Buf[_BUF_SIZE];
pointer _Ptr;
char _Alias[_BUF_SIZE];
};
_Bxty _Bx;
// invariant: _Myres >= _Mysize, and _Myres >= _Small_string_capacity (after string's construction)
// neither _Mysize nor _Myres takes account of the extra null terminator
size_type _Mysize = 0; // current length of string (size)
size_type _Myres = 0; // current storage reserved for string (capacity)
};
无关部分:__compressed_pair 相当于封装了 EBO,和 libstdc++ 手写的 _Alloc_hider 差不多意思,本文不讨论;MSVC STL 中只要是容器,_Container_base 都会继承它,感兴趣可以看 xmemory 文件,略。
MSVC STL 的 std::string 显然和 libstdc++ 不同,它的 SSO buffer 复用了 data pointer(见 _Bxty)。至于 SSO 阈值和 sizeof 大小,则分别是 16 和 32,和 libstdc++ 一样。
运行时布局
_CONSTEXPR20
basic_string() /*noexcept(...)*/ : _Mypair(_Zero_then_variadic_args_t{}) {
/// _Construct_empty():
auto& _My_data = _Mypair._Myval2;
_My_data._Alloc_proxy(_STD _Get_proxy_allocator(_Getal()));
// initialize basic_string data members
_My_data._Mysize = 0;
_My_data._Myres = _Small_string_capacity;
_My_data._Activate_SSO_buffer();
// the _Traits::assign is last so the codegen doesn't think the char write can alias this
_Traits::assign(_My_data._Bx._Buf[0], _Elem());
}
_CONSTEXPR20 basic_string(_In_reads_(_Count) const _Elem* const _Ptr, const size_type _Count)
: _Mypair(_Zero_then_variadic_args_t{}) {
_Construct<_Construct_strategy::_From_ptr>(_Ptr, _Count);
}
NOTES:
- 接受
const char *的构造函数实际展开会很长(生活不止 SSO!),你需要知道超过 SSO 阈值才会动用 data pointer 就是了。 - 关于 compressed pair 的初始化细节见这里。
运行时开销
_NODISCARD _CONSTEXPR20 _Ret_z_ const _Elem* data() const noexcept {
/// return _Mypair._Myval2._Myptr();
const value_type* _Result = _Bx._Buf;
if (_Large_mode_engaged()) { // _Myres > _Small_string_capacity
_Result = _Unfancy(_Bx._Ptr);
}
return _Result;
}
_NODISCARD _CONSTEXPR20 size_type size() const noexcept {
return _Mypair._Myval2._Mysize;
}
_NODISCARD _CONSTEXPR20 size_type capacity() const noexcept {
return _Mypair._Myval2._Myres;
}
MSVC STL 的 std::string 是要在 data() 寻址付出代价的,也就是说会牵连到 operator[]。
不太清楚微软怎么想的……
libc++
结论先行
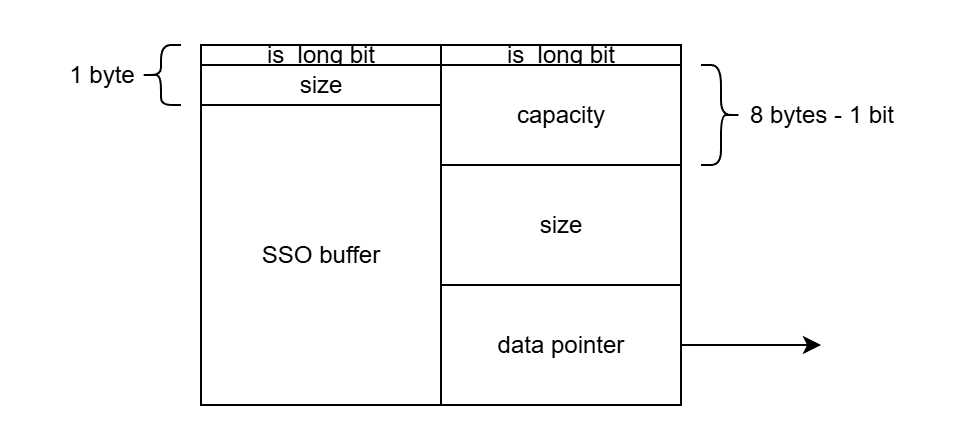 位置有点挤,画不出真实比例关系……
位置有点挤,画不出真实比例关系……
对于内存占用,libc++ 的 std::string 静态内存布局占用 24 字节,SSO 阈值高达 23 字节!(含 '\0')libc++ 使用两个完全不同的结构体去描述 short 和 long 场景。这里 libc++ 聪明在于,它知道 SSO 模式下使用 uint8 来维护大小是足够的,并且能进一步塞入 is long bit。
对于初始化的运行时内存布局,这方面没有特别的,判断 small 和 large 区分即可。
对于运行时开销,所有操作均存在分支去判断 small 和 long。
内存布局
template <class _CharT, class _Traits, class _Allocator>
class basic_string {
#ifdef _LIBCPP_ABI_ALTERNATE_STRING_LAYOUT
struct __long {
pointer __data_;
size_type __size_;
size_type __cap_ : sizeof(size_type) * CHAR_BIT - 1;
size_type __is_long_ : 1;
};
enum {
__min_cap =
(sizeof(__long) - 1) / sizeof(value_type) > 2 ? (sizeof(__long) - 1) / sizeof(value_type) : 2
};
struct __short {
value_type __data_[__min_cap];
unsigned char __padding_[sizeof(value_type) - 1];
unsigned char __size_ : 7;
unsigned char __is_long_ : 1;
};
#else
struct __long {
struct _LIBCPP_PACKED {
size_type __is_long_ : 1;
size_type __cap_ : sizeof(size_type) * CHAR_BIT - 1;
};
size_type __size_;
pointer __data_;
};
enum {
__min_cap =
(sizeof(__long) - 1) / sizeof(value_type) > 2 ? (sizeof(__long) - 1) / sizeof(value_type) : 2
};
struct __short {
struct _LIBCPP_PACKED {
unsigned char __is_long_ : 1;
unsigned char __size_ : 7;
};
char __padding_[sizeof(value_type) - 1];
value_type __data_[__min_cap];
};
#endif
union __ulx {
__long __lx;
__short __lxx;
};
enum { __n_words = sizeof(__ulx) / sizeof(size_type) };
struct __raw {
size_type __words[__n_words];
};
struct __rep {
union {
__short __s;
__long __l;
__raw __r;
};
};
__compressed_pair<__rep, allocator_type> __r_;
};
注意 libc++ 存在两种 ABI 布局,如果选用更加激进的 _LIBCPP_ABI_ALTERNATE_STRING_LAYOUT(非默认),这会使得 __data_ 总是在首部,并且会占用 32 字节。config 中提到是为了尽可能对齐。
运行时布局
_LIBCPP_HIDE_FROM_ABI _LIBCPP_CONSTEXPR_SINCE_CXX20 basic_string()
_NOEXCEPT_(is_nothrow_default_constructible<allocator_type>::value)
: __r_(__value_init_tag(), __default_init_tag()) {}
template <__enable_if_t<__is_allocator<_Allocator>::value, int> = 0>
_LIBCPP_HIDE_FROM_ABI _LIBCPP_CONSTEXPR_SINCE_CXX20 basic_string(const _CharT* __s)
: __r_(__default_init_tag(), __default_init_tag()) {
_LIBCPP_ASSERT_NON_NULL(__s != nullptr, "basic_string(const char*) detected nullptr");
/// __init(__s, traits_type::length(__s)):
size_type __sz = traits_type::length(__s);
if (__libcpp_is_constant_evaluated())
__r_.first() = __rep();
if (__sz > max_size())
__throw_length_error();
pointer __p;
if (__fits_in_sso(__sz)) { // __sz < __min_cap
__r_.first().__s.__size_ = __sz;
__r_.first().__s.__is_long_ = false;
__p = __get_short_pointer();
} else {
auto __allocation = std::__allocate_at_least(__alloc(), __recommend(__sz) + 1);
__p = __allocation.ptr;
__begin_lifetime(__p, __allocation.count);
__set_long_pointer(__p);
__set_long_cap(__allocation.count);
__set_long_size(__sz);
}
traits_type::copy(std::__to_address(__p), __s, __sz);
traits_type::assign(__p[__sz], value_type());
}
展开太复杂了,总之都是基操。
运行时开销
_LIBCPP_HIDE_FROM_ABI _LIBCPP_CONSTEXPR_SINCE_CXX20 const value_type* data() const _NOEXCEPT {
return std::__to_address(__is_long() ? __get_long_pointer() : __get_short_pointer());
}
_LIBCPP_HIDE_FROM_ABI _LIBCPP_CONSTEXPR_SINCE_CXX20 size_type size() const _NOEXCEPT {
return __is_long() ? __get_long_size() : __get_short_size();
}
_LIBCPP_HIDE_FROM_ABI _LIBCPP_CONSTEXPR_SINCE_CXX20 size_type capacity() const _NOEXCEPT {
return (__is_long() ? __get_long_cap() : static_cast<size_type>(__min_cap)) - 1;
}
folly
结论先行
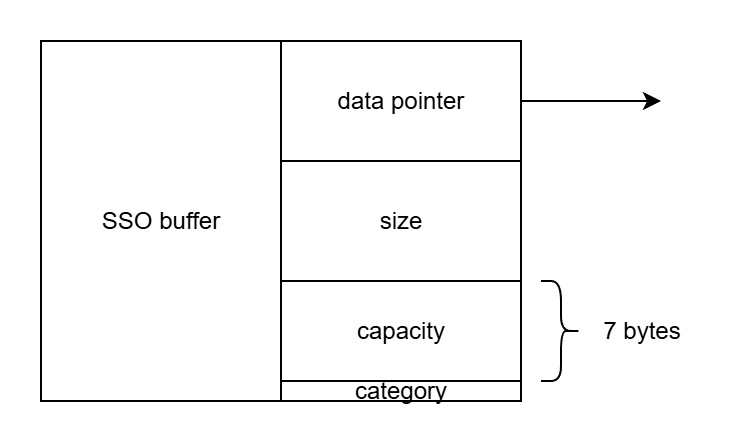
对于内存占用,folly 的 fbstring 静态内存布局占用 24 字节(8+8+7+1),SSO 阈值可以做到完整的 24 字节!(含 '\0')
这里实现的技巧在于 SSO buffer 的最后一个字节,它的数值描述为 capacity - size。这意味着当 SSO buffer 缓冲的长度为 23 时,恰好最后一个字节的数值为 0,既能作为 '\0',也能表示 size 已到达 capacity。
对于初始化的运行时内存布局,fbstring 不同于标准库的实现,采用了 small/medium/large 的场景区分,其中 large 还会采用 copy on write 设计,而前两个场景就类似此前的 std::string。
对于运行时开销,所有操作均存在分支(通过 category 字节)去判断场景。具体成本 small 最低,large 最高。
注:category 字节同时作为 SSO buffer char、current - size 和 is_meidum_large_flag 的类型双(三)关设计。
内存布局
/**
* This is the core of the string. The code should work on 32- and
* 64-bit and both big- and little-endianan architectures with any
* Char size.
*
* The storage is selected as follows (assuming we store one-byte
* characters on a 64-bit machine): (a) "small" strings between 0 and
* 23 chars are stored in-situ without allocation (the rightmost byte
* stores the size); (b) "medium" strings from 24 through 254 chars
* are stored in malloc-allocated memory that is copied eagerly; (c)
* "large" strings of 255 chars and above are stored in a similar
* structure as medium arrays, except that the string is
* reference-counted and copied lazily. the reference count is
* allocated right before the character array.
*
* The discriminator between these three strategies sits in two
* bits of the rightmost char of the storage:
* - If neither is set, then the string is small. Its length is represented by
* the lower-order bits on little-endian or the high-order bits on big-endian
* of that rightmost character. The value of these six bits is
* `maxSmallSize - size`, so this quantity must be subtracted from
* `maxSmallSize` to compute the `size` of the string (see `smallSize()`).
* This scheme ensures that when `size == `maxSmallSize`, the last byte in the
* storage is \0. This way, storage will be a null-terminated sequence of
* bytes, even if all 23 bytes of data are used on a 64-bit architecture.
* This enables `c_str()` and `data()` to simply return a pointer to the
* storage.
*
* - If the MSb is set, the string is medium width.
*
* - If the second MSb is set, then the string is large. On little-endian,
* these 2 bits are the 2 MSbs of MediumLarge::capacity_, while on
* big-endian, these 2 bits are the 2 LSbs. This keeps both little-endian
* and big-endian fbstring_core equivalent with merely different ops used
* to extract capacity/category.
*/
template <class Char>
class fbstring_core {
struct MediumLarge {
Char* data_;
size_t size_;
size_t capacity_;
};
union {
uint8_t bytes_[sizeof(MediumLarge)]; // For accessing the last byte.
Char small_[sizeof(MediumLarge) / sizeof(Char)];
MediumLarge ml_;
};
};
template <
typename E,
class T = std::char_traits<E>,
class A = std::allocator<E>,
class Storage = fbstring_core<E>>
class basic_fbstring {
// Data
Storage store_;
};
这里注释已经写得很清楚了。SSO 拉满的技巧在于 max_size - size。
运行时布局
前面文档说得很清楚了,有三种:[0, 24), [24, 255), [255, …)。
运行时开销
// 核心操作全部依赖于 category byte
Category category() const {
// works for both big-endian and little-endian
return static_cast<Category>(bytes_[lastChar] & categoryExtractMask);
}
////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
const value_type* fbstring_core::data() const {
const Char* ptr = ml_.data_;
// With this syntax, GCC and Clang generate a CMOV instead of a branch.
ptr = (category() == Category::isSmall) ? small_ : ptr;
return ptr;
}
size_type fbstring_core::size() const {
size_t ret = ml_.size_;
if constexpr (kIsLittleEndian) {
// We can save a couple instructions, because the category is
// small iff the last char, as unsigned, is <= maxSmallSize.
typedef typename std::make_unsigned<Char>::type UChar;
auto maybeSmallSize = size_t(maxSmallSize) -
size_t(static_cast<UChar>(small_[maxSmallSize]));
// With this syntax, GCC and Clang generate a CMOV instead of a branch.
ret =
(static_cast<ptrdiff_t>(maybeSmallSize) >= 0) ? maybeSmallSize : ret;
} else {
ret = (category() == Category::isSmall) ? smallSize() : ret;
}
return ret;
}
size_t capacity() const {
// 看不懂
}
0000000000000000 <_Z9test_datav>:
0: 48 8b 05 00 00 00 00 mov 0x0(%rip),%rax // %rax 是 fbstring 的地址
7: 80 78 17 40 cmpb $0x40,0x17(%rax) // 比较 偏移 0x17(十进制 23)的字节与 0x40 的关系
b: 72 03 jb 10 <_Z9test_datav+0x10> // 如果是 small,那么当前的 %rax 就可以充当 SSOB 地址
d: 48 8b 00 mov (%rax),%rax // 否则,解引用 data pointer(刚好在开头),指向堆
10: c3 ret // 显然,前面 Clang 并没有产生 cmov,源码注释说得不对
11: 66 66 66 66 66 66 2e data16 data16 data16 data16 data16 cs nopw 0x0(%rax,%rax,1)
18: 0f 1f 84 00 00 00 00
1f: 00
0000000000000020 <_Z9test_sizev>:
20: 48 8b 05 00 00 00 00 mov 0x0(%rip),%rax
27: 0f b6 48 17 movzbl 0x17(%rax),%ecx // 还是 category 字节,作为零扩展范围长字赋值
2b: 48 83 f9 18 cmp $0x18,%rcx // 比较数值 24
2f: 72 05 jb 36 <_Z9test_sizev+0x16> // small 场景,跳转,后续倒过来减去 23 返回
31: 48 8b 40 08 mov 0x8(%rax),%rax // medium/large 场景,获取 size 字段返回
35: c3 ret
36: b8 17 00 00 00 mov $0x17,%eax
3b: 48 29 c8 sub %rcx,%rax
3e: c3 ret
3f: 90 nop
0000000000000040 <_Z13test_capacityv>: // 这个太复杂了……知道分支、访存和计算都很多即可
40: 48 8b 0d 00 00 00 00 mov 0x0(%rip),%rcx
47: 0f b6 41 17 movzbl 0x17(%rcx),%eax7
4b: 25 c0 00 00 00 and $0xc0,%eax // category 字节只拿高两位(MSB)
50: 74 26 je 78 <_Z13test_capacityv+0x38> // 如果高两位为空,如文档所言,就是 small
52: 83 f8 40 cmp $0x40,%eax // 这里应该是看 medium/large,中间是要处理引用计数的,略
55: 75 12 jne 69 <_Z13test_capacityv+0x29> // 应该是 medium 会跳?没有 second MSB
57: 48 8b 01 mov (%rcx),%rax
5a: 48 8b 40 f8 mov -0x8(%rax),%rax
5e: 48 83 f8 02 cmp $0x2,%rax
62: 72 05 jb 69 <_Z13test_capacityv+0x29>
64: 48 8b 41 08 mov 0x8(%rcx),%rax
68: c3 ret
69: 48 b8 ff ff ff ff ff movabs $0x3fffffffffffffff,%rax // medium 跳转过来,抹除 MSB 两位
70: ff ff 3f
73: 48 23 41 10 and 0x10(%rcx),%rax // 大概是 capacity & MASK(0x3ff...)
77: c3 ret
78: b8 17 00 00 00 mov $0x17,%eax // small 跳转过来,直接返回固定的数值 23
7d: c3 ret
与此前的 godbolt 测试方法相同,只是换成了 folly::fbstring。看源码好像有点复杂,所以尝试直接 dump 下来,可以直观看出 -O3 运行时成本:large 是很夸张的,访存、比较和计算全都占了。
总结
| 特性 | libstdc++ | MSVC STL | libc++ | folly::fbstring |
|---|---|---|---|---|
sizeof(string)
| 32 字节 | 32 字节 | 24 字节 | 24 字节 |
SSO 阈值(包含 '\0')
| 16 字节 | 16 字节 | 23 字节 | 24 字节 |
data() 开销
| 零额外开销 | 分支判断 | 分支判断 | 分支判断 |
size() 开销
| 零额外开销 | 零额外开销 | 分支判断 | 分支判断 |
capacity() 开销
| 分支判断 | 零额外开销 | 分支判断 | 复杂分支 |
| 核心技巧 | SSOB 复用 capacity | SSOB 复用 data pointer | is_long bit | category byte 结束符重用 |
| 其他特性 | constexpr unfriendly | 只存在于 Windows | 多种 ABI 布局 | small/medium/large,CoW,感觉很厉害 |